Belt Dryer vs Tray Dryer
When it comes to industrial drying processes, choosing the right equipment is crucial for achieving efficient and consistent results. Among the most commonly used drying systems in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and more, the belt dryer and tray dryer are two popular options. Both serve the same basic function—drying materials—but they do so in distinct ways, each with its advantages and drawbacks.

In this article, we will compare belt dryer vs tray dryer, discussing their working principles, applications, benefits, and limitations. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of which drying method might be best suited for your specific needs.
What is a Belt Dryer?
A belt dryer is a continuous drying system that uses a moving belt to carry the product through a heated drying chamber. The product is typically spread evenly on a conveyor belt, where it is exposed to hot air or other forms of heat that cause the moisture to evaporate. Belt dryers are commonly used in industries that require bulk drying of materials like vegetables, fruits, chemicals, and various food products.
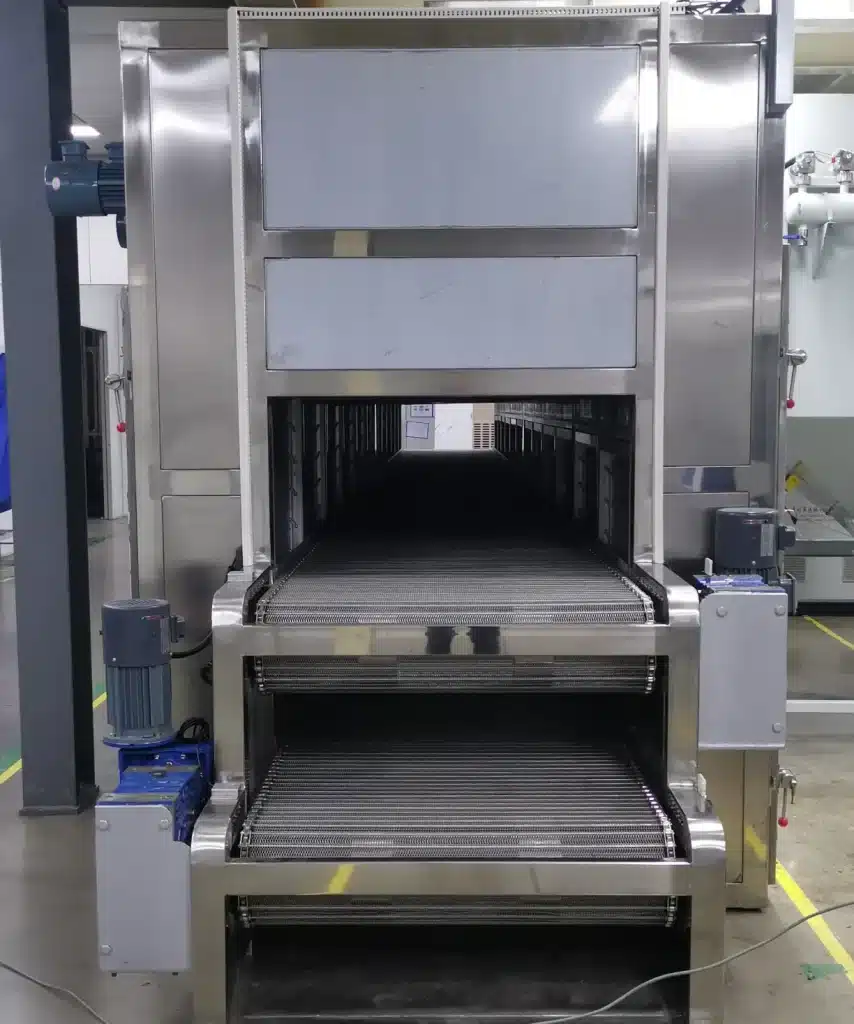

Key Features of a Belt Dryer:
- Continuous Process: Belt dryers operate on a continuous basis, which allows for high throughput.
- Even Heat Distribution: The design of the conveyor belt ensures that the material is exposed to a consistent airflow, promoting even drying.
- Large Capacity: Belt dryers are ideal for drying large quantities of material in a relatively short period.
- Modular Design: They can be customized in terms of length and number of drying zones to suit specific material requirements.
Applications of Belt Dryers:
- Food Processing: Drying fruits, vegetables, herbs, and grains.
- Chemical Industry: Drying powders, granules, and crystals.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Drying active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other compounds.
- Waste Treatment: Drying sludge, bio-mass, and other waste materials.
What is a Tray Dryer?
A tray dryer, also known as a batch dryer, is a type of drying equipment where the product is placed in trays, which are then loaded into a drying chamber. Hot air is circulated in the chamber, and moisture is removed from the material over time. The drying process is batch-based, meaning that the material is loaded and unloaded in distinct cycles.
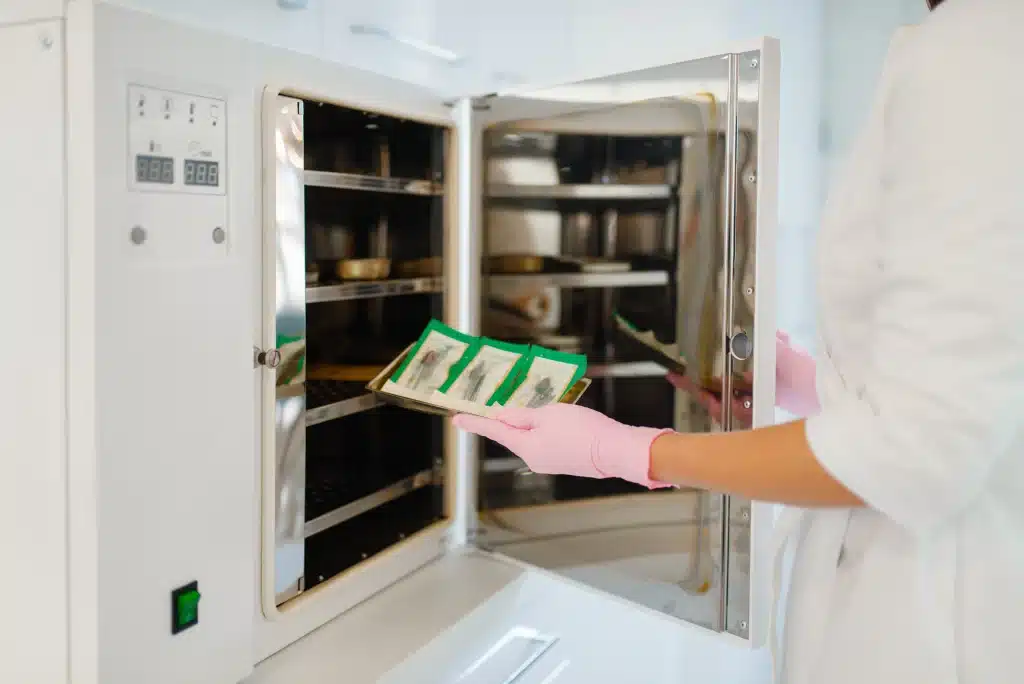

Key Features of a Tray Dryer:
- Batch Process: Tray dryers operate in batches, meaning they are ideal for smaller quantities or when production cycles need to be flexible.
- Versatility: Tray dryers can handle a variety of products, including bulk solids, powders, and even liquids in some cases.
- Simple Operation: They are relatively straightforward to operate and maintain.
- Energy Efficiency: Tray dryers tend to use less energy in situations where drying demand is intermittent or low.
Applications of Tray Dryers:
- Pharmaceuticals: Drying of powders, granules, and pills.
- Food Industry: Drying of herbs, spices, and small quantities of fruit or vegetables.
- Chemicals: Drying of fine powders, resins, and other sensitive materials.
- Laboratory Use: Often used for drying samples in research and development settings.
Belt Dryer vs Tray Dryer: Key Differences
1. Drying Process: Continuous vs. Batch
The primary distinction between the two dryers lies in their operation mode. Belt dryers use a continuous drying process, where materials move along a conveyor belt through a series of drying zones. This continuous operation makes belt dryers ideal for high-volume, industrial applications.
In contrast, tray dryers operate on a batch process. Materials are loaded onto trays and placed in the drying chamber for a fixed period. After drying, the trays are removed and the process starts over. Tray dryers are better suited for smaller quantities or when flexibility in batch sizes is needed.
2. Capacity
Due to the continuous nature of the belt dryer, it generally has a higher drying capacity compared to a tray dryer. Belt dryers are capable of handling large volumes of material simultaneously, which makes them more efficient for industries with high production demands.
Tray dryers, being batch-based, tend to have a lower capacity. The process requires loading and unloading, which can limit throughput. However, they provide greater flexibility in managing smaller batches or specific drying requirements.
3. Heat Transfer and Uniformity
Belt dryers are designed to provide uniform heat distribution across the material, as it is spread evenly on the conveyor belt. The heated air is evenly circulated over the material, ensuring consistent drying. This makes them ideal for materials that need even moisture removal.
On the other hand, tray dryers rely on hot air circulation within the chamber. The drying efficiency can be affected by the placement of trays, as materials in the upper trays may receive more heat than those in lower trays. This can result in uneven drying unless special provisions like rotating trays are used.
4. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency depends on the specific requirements of the drying process. Tray dryers are typically more energy-efficient for smaller batches, as they do not need to run continuously. They also tend to have lower energy consumption because they are usually smaller and more compact.
Belt dryers, with their continuous operation, tend to use more energy, especially in large-scale applications. However, modern belt dryers are designed with energy-saving features like heat recovery systems, which can help offset some of the higher energy costs.
5. Material Handling and Flexibility
Belt dryers are ideal for materials that can be spread evenly across a belt. This makes them less versatile for irregularly shaped materials or products that are sensitive to handling. Products like fruits, vegetables, and granular substances typically perform best in belt dryers.
Tray dryers, on the other hand, offer greater flexibility in terms of material handling. Since the product is placed in trays, you can easily dry different types of materials, including powders, liquids, and delicate items that may be damaged by continuous motion.
6. Cost and Maintenance
Tray dryers are generally more affordable than belt dryers, both in terms of initial investment and maintenance. They are simpler machines with fewer moving parts, making them easier to maintain and repair.
Belt dryers tend to be more expensive, especially for large-scale industrial applications. The maintenance of conveyor systems, heating elements, and fans can add to the operational cost. However, their high throughput and efficiency can offset the initial costs over time.

Belt Dryer vs Tray Dryer: Which is Better for Your Business?
Choosing between a belt dryer vs tray dryer largely depends on your specific needs and production requirements. Below are some factors to consider when making your decision:
- Scale of Operation: If you’re handling large quantities of material on a continuous basis, a belt dryer is likely the better option. For smaller, flexible batches, a tray dryer will suffice.
- Material Type: If you’re working with materials that need gentle handling or are irregularly shaped, a tray dryer might be more appropriate. Belt dryers are better suited for bulk materials that can be spread evenly.
- Energy Considerations: If energy efficiency is a concern and you have smaller batches, tray dryers could be the more energy-efficient choice. Belt dryers, while efficient in large-scale operations, may consume more energy.
- Cost Constraints: Tray dryers are typically more affordable and easier to maintain. However, if your business requires high throughput, investing in a belt dryer may offer better long-term value.
In the debate of belt dryer vs tray dryer, there is no one-size-fits-all answer.
Both systems offer distinct advantages and are suited for different applications. Belt dryers are ideal for large-scale, continuous drying processes, offering high throughput and uniformity. Tray dryers, on the other hand, offer more flexibility and lower energy consumption, making them suitable for smaller, batch-based operations.
Understanding your production requirements, material characteristics, and energy constraints will help you make the right choice for your business. Whether you opt for a belt dryer or a tray dryer, both systems have proven themselves essential in various industries, offering reliable drying solutions that meet the demands of modern manufacturing and processing.
Ivey excels in effectively conveying company directives through impactful marketing and public relations strategies, showcasing her expertise in the field.
Email: ivey.tang@sinothermo.com
Phone: +86 19105155639