Understanding the Different Types of Convection Dryers
Convection dryers are essential equipment in various industries, particularly in the food, chemical, pharmaceutical, and manufacturing sectors. These dryers are used to remove moisture from materials by using hot air or gases, which circulate around the material. The heat from the air evaporates the moisture, leaving the material dry and ready for further processing. There are several types of convection dryers, each designed to meet specific drying needs. In this article, we will explore the different types of convection dryers, including Belt Dryers, Tray Dryers, Rotary Kilns, Flash Dryers, Spray Dryers, Vibrating Dryers, and Fluidized Bed Dryers.

1. Belt Dryer
A belt dryer is one of the most commonly used convection dryers in industries requiring high-volume drying. It operates by moving the material on a continuous conveyor belt while hot air is blown over it. The material typically moves through several drying zones where the air temperature and airflow speed can be controlled to optimize the drying process.
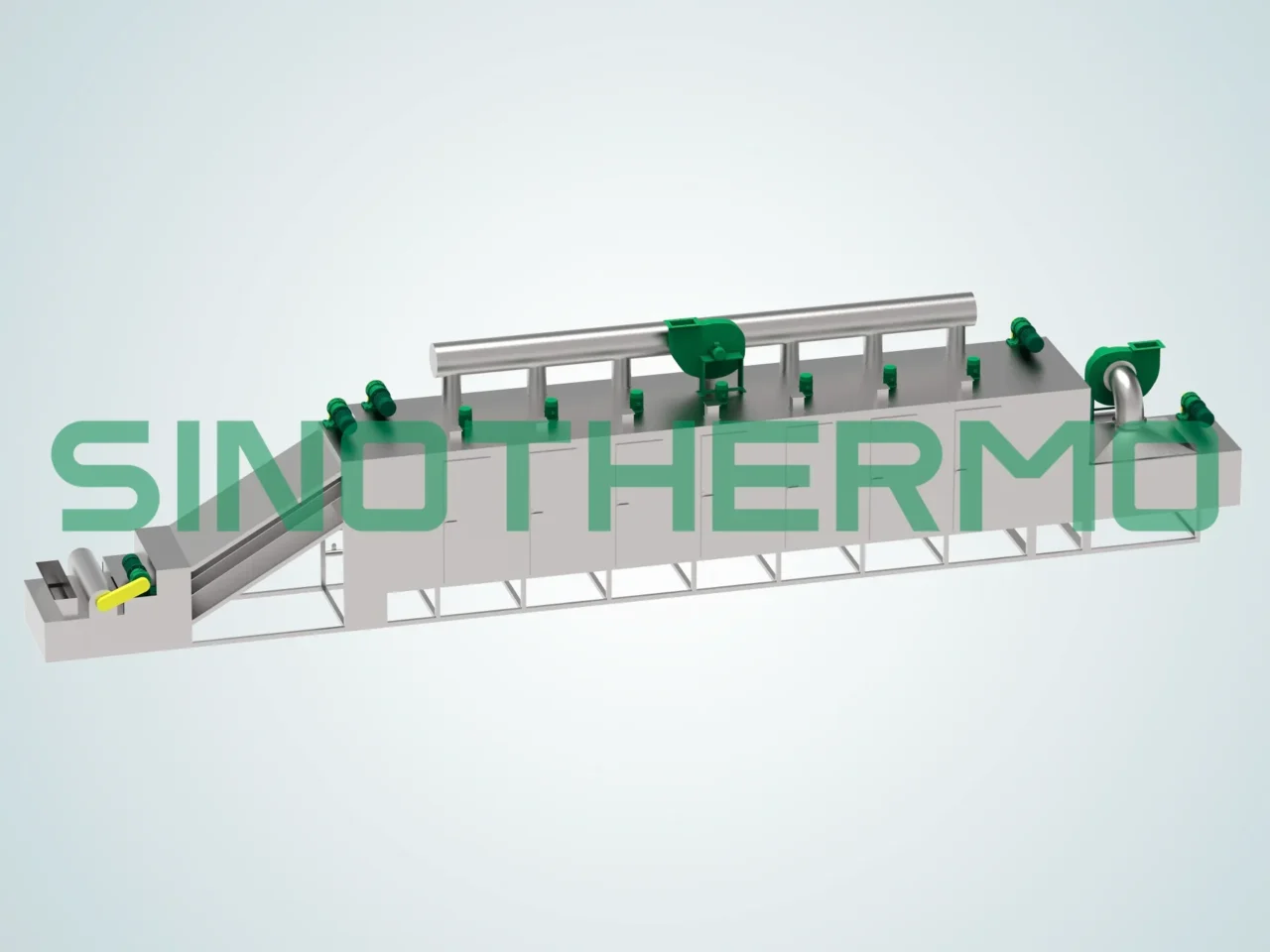
Features of Belt Dryers:
- Continuous Operation: The material moves along the belt in a continuous flow, making it ideal for large-scale production.
- Energy Efficient: Due to the continuous process, belt dryers are highly energy-efficient.
- Adjustable Airflow: The airflow and temperature can be adjusted according to the material’s requirements.
Applications:
- Food processing (e.g., drying fruits, vegetables, and meat products)
- Wood and paper drying
- Chemical processing
2. Tray Dryer
A tray dryer is another popular type of convection dryer that is used in smaller batches or for more delicate materials. In a tray dryer, the material is placed in trays or shelves, and hot air is passed through these trays to remove the moisture. The trays can be stacked vertically, allowing for efficient use of space.

Features of Tray Dryers:
- Batch Processing: Tray dryers operate in batches, making them ideal for materials that need to be dried in small quantities.
- Gentle Drying: The controlled airflow and heat are ideal for drying delicate materials without causing damage.
- Compact Design: Tray dryers have a compact design, which makes them suitable for laboratories or small-scale production units.
Applications:
- Pharmaceutical industries (e.g., drying powders and granules)
- Food processing (e.g., drying herbs, spices, and small amounts of fruits)
- Laboratory and research settings
3. Rotary Kiln
A rotary kiln is a large, cylindrical device used in the drying and processing of materials, especially in the cement, mineral, and chemical industries. In a rotary kiln, the material is continuously fed into the cylinder, which rotates while hot gases pass through the material. The rotating action ensures that the material is evenly dried.
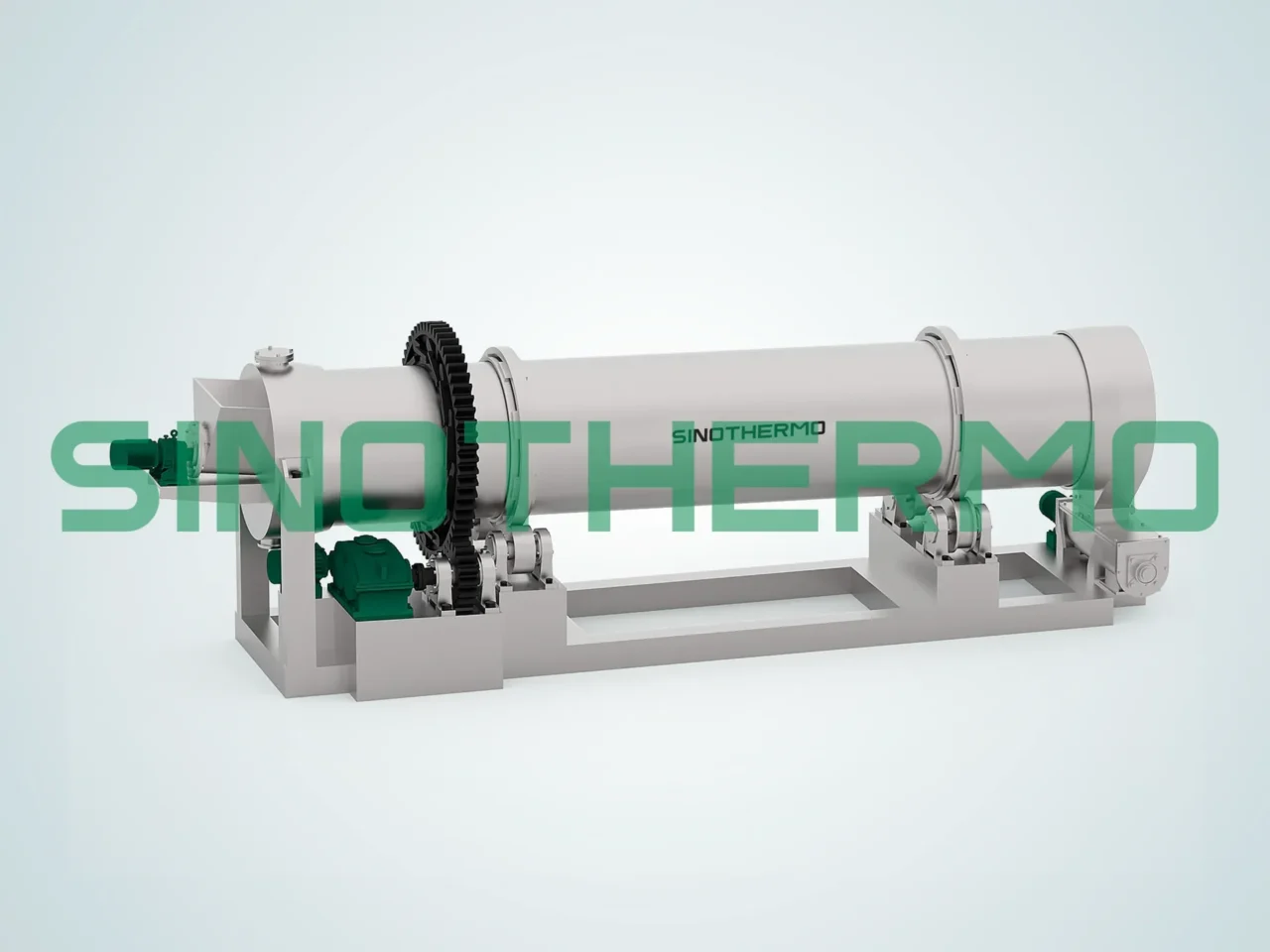

Features of Rotary Kilns:
- High Capacity: Rotary kilns are ideal for large-scale production due to their high capacity and continuous processing.
- Uniform Drying: The rotation of the cylinder ensures that the material is evenly exposed to the hot air.
- High Temperature Resistance: Rotary kilns can handle very high temperatures, making them suitable for drying materials like minerals or chemicals.
Applications:
- Cement production
- Chemical processing
- Mineral drying
4. Flash Dryer
A flash dryer is a rapid drying system that uses a high-speed airflow to instantly dry materials. In this system, the material is exposed to hot air, which causes moisture to evaporate almost immediately. Flash dryers are particularly effective for drying fine powders or small particles.

Features of Flash Dryers:
- Instant Drying: Flash dryers use high-speed air to rapidly remove moisture from the material.
- Compact Design: These dryers are typically compact and take up less space compared to other types.
- Suitable for Fine Particles: Flash dryers are ideal for drying fine powders and small particles.
Applications:
- Food processing (e.g., drying instant coffee or powdered milk)
- Pharmaceutical industries (e.g., drying active pharmaceutical ingredients)
- Chemical industries (e.g., drying fine chemicals)
5. Spray Dryer
A spray dryer is a specialized type of convection dryer that converts liquids into dry powders. In this system, the liquid material is atomized into fine droplets and then exposed to a stream of hot air. The hot air evaporates the moisture, leaving behind dry particles. Spray dryers are commonly used for drying liquid foods, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
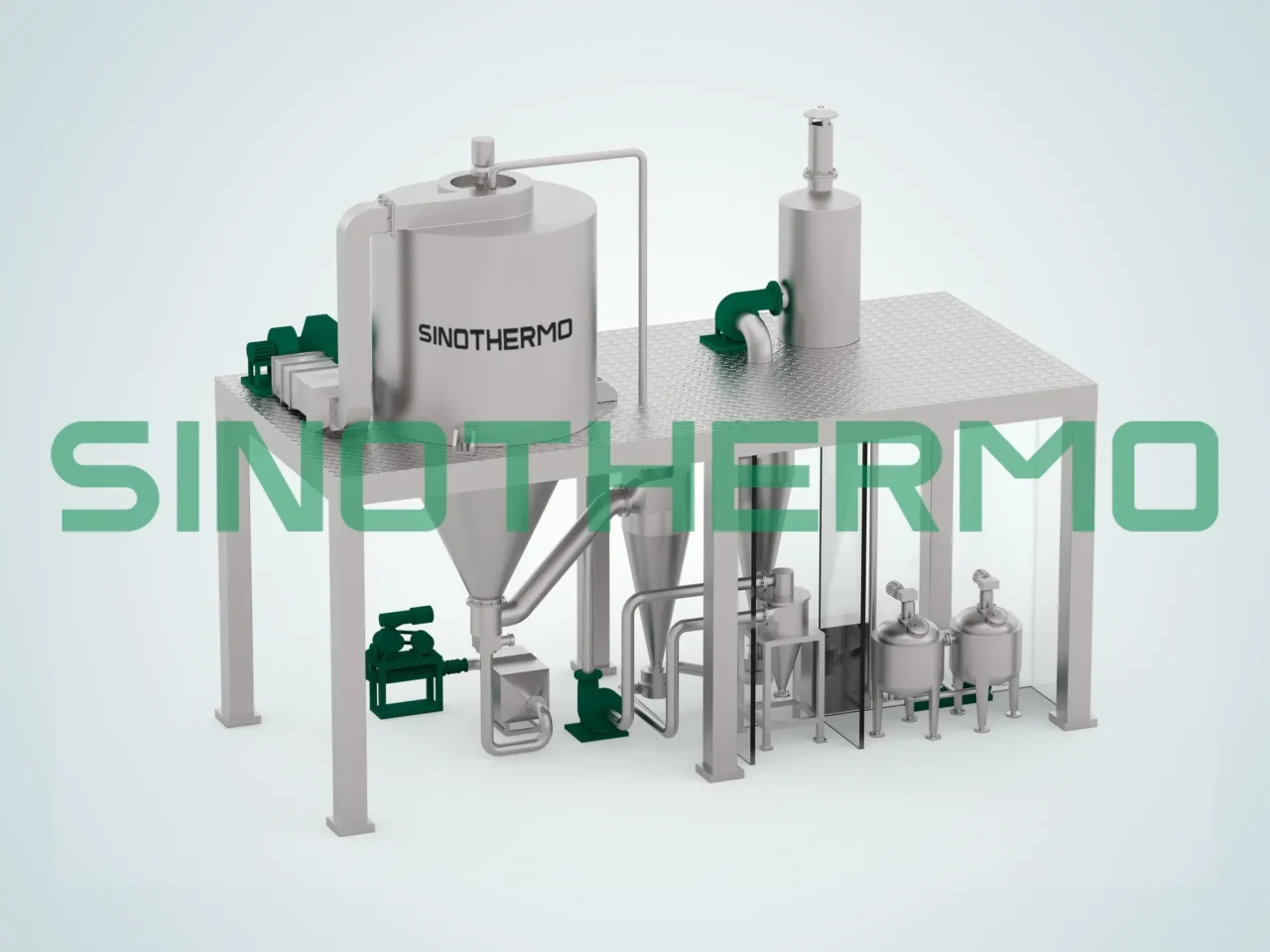

Features of Spray Dryers:
- Fine Powder Production: Spray dryers are ideal for producing fine powders from liquids.
- High Efficiency: The rapid evaporation process makes spray dryers highly efficient in terms of time and energy.
- Precise Control: The temperature, air pressure, and droplet size can be precisely controlled for optimal drying conditions.
Applications:
- Dairy industry (e.g., powdered milk, whey powder)
- Pharmaceuticals (e.g., drying vaccines or proteins)
- Food industry (e.g., instant soups, baby foods)
6. Vibrating Dryer
A vibrating dryer uses vibration to move the material along the drying chamber while hot air circulates around it. The vibrating action helps to agitate the material, ensuring even exposure to the drying air. This type of dryer is commonly used for drying granular or powdery materials.

Features of Vibrating Dryers:
- Uniform Drying: The vibration ensures that the material moves continuously, leading to uniform drying.
- Efficient Airflow: Hot air circulates efficiently around the material due to the vibration.
- Low Energy Consumption: Vibrating dryers are typically energy-efficient because they require less mechanical force compared to other drying systems.
Applications:
- Drying granular chemicals
- Food processing (e.g., drying sugar, salt)
- Pharmaceutical applications
7. Fluidized Bed Dryer
A fluidized bed dryer is a system in which the material is suspended in a flow of hot air. The air flow makes the material behave like a fluid, ensuring that all surfaces are exposed to the drying air. This type of dryer is highly effective for drying fine powders and granular materials.
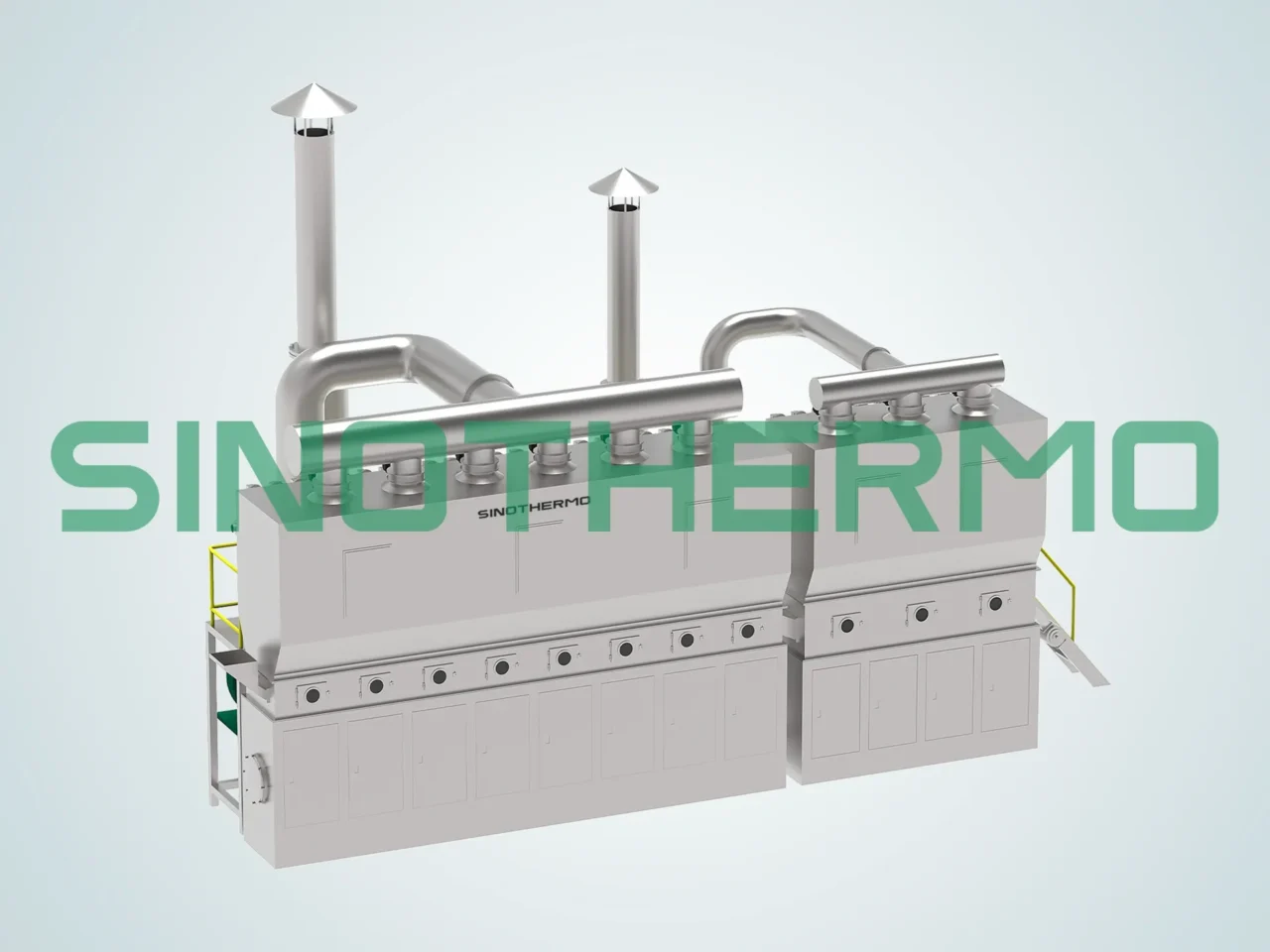

Features of Fluidized Bed Dryers:
- Uniform Drying: The material is suspended in the air, ensuring even heat distribution.
- High Heat Transfer: The direct contact between the material and the hot air results in efficient heat transfer.
- Energy Efficient: Fluidized bed dryers are known for their low energy consumption due to their efficient drying process.
Applications:
- Food industry (e.g., drying spices, herbs)
- Pharmaceutical industry (e.g., drying powders, granules)
- Chemical industry (e.g., drying catalysts)
Different Types of Convection Dryers
whether it’s the belt dryer, tray dryer, rotary kiln, flash dryer, spray dryer, vibrating dryer, or fluidized bed dryer—offers distinct advantages based on the specific needs of the material being dried. By understanding their unique features and applications, industries can make more informed decisions about which dryer best suits their production processes. Whether you’re dealing with large-scale bulk drying or precision drying of fine powders, there’s a convection dryer designed to deliver the efficiency, speed, and quality you need to enhance your operations. Selecting the right system ensures optimal performance, energy savings, and high-quality dried products, paving the way for better productivity and cost-effectiveness in the long run.
Ivey excels in effectively conveying company directives through impactful marketing and public relations strategies, showcasing her expertise in the field.
Email: ivey.tang@sinothermo.com
Phone: +86 19105155639