What is a Convection Dryer?
A convection dryer is a type of industrial drying equipment that utilizes the principles of convective heat transfer to remove moisture from materials. As described by ScienceDirect, convective drying is “the most widely used dehydration method which is considered as the simultaneous heat and mass transfer phenomena.”
The convection drying process involves exposing the wet material to a stream of hot air or steam, which facilitates the evaporation of moisture from the surface of the material. The resulting water vapor is then carried away by the airflow, leaving behind a dried product.
There are three main types of convection dryers:
- Belt Dryers: Materials are spread on a conveyor belt and passed through a heated chamber where hot air circulates around them.
- Drum Dryers: The wet material is fed into a rotating drum through which hot air is circulated, causing the moisture to evaporate.
- Fluid Bed Dryers: The material is suspended and agitated in a stream of hot air, allowing for efficient drying and heat transfer.
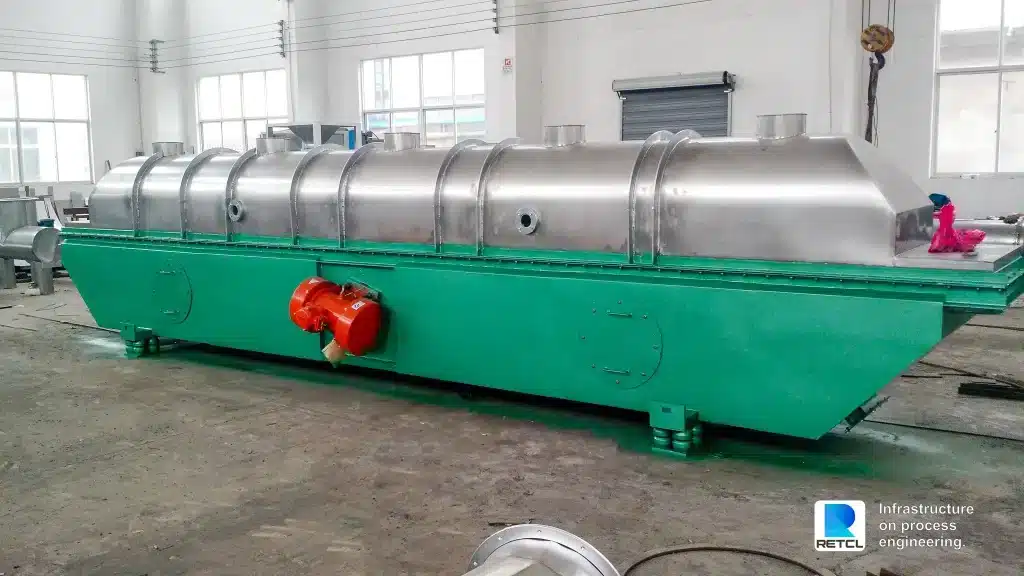

How Convection Dryers Work
Convection dryers utilize the principles of convective heat transfer to remove moisture from materials. Hot air or steam is circulated over the wet product, initiating simultaneous heat and mass transfer. As the hot air flows over the material’s surface, it picks up moisture, carrying it away from the product.
Airflow patterns and circulation are crucial in convection drying. The air is typically drawn into the dryer by a fan, heated by a burner or heat exchanger, then forced through the bed of material. Proper airflow design ensures uniform drying across the entire product bed. Techniques like airflow reversal or multi-directional airflow promote even moisture removal from all surfaces. Source
Heat transfer in convection dryers occurs primarily through convection from the hot air to the material surface. As the surface moisture evaporates, heat conducts further into the product to drive off internal moisture. The heating medium can be hot air, combustion gases, or a heat transfer fluid like steam or thermal oil circulating through coils.
Typical heating methods include direct-fired burners using gas or oil, indirect heating via steam coils or thermal fluid, or electric element heating. The heat source must provide sufficient energy input to maintain the desired drying air temperature and airflow rate for the specific application.
Benefits of Convection Drying
Convection dryers offer several advantages over other drying methods, making them an attractive choice for various industrial applications:
1. Fast, Efficient Moisture Removal: The circulation of hot air or steam in convection dryers facilitates rapid and uniform moisture evaporation from the material being dried. This results in shorter drying times and improved throughput compared to other methods like conductive or infrared drying. Source
2. Uniform Drying: The constant airflow and heat transfer in convection dryers ensure that the material is dried evenly throughout, preventing over-drying or under-drying in certain areas. This uniformity leads to consistent product quality and minimizes waste.
3. Flexible Batch Sizes: Convection dryers can accommodate a wide range of batch sizes, from small lab-scale batches to large industrial volumes, making them versatile for various production needs.
4. Low Maintenance: Compared to other drying methods, convection dryers have relatively simple designs with few moving parts, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and downtime.
5. Energy Efficient: By relying on the transfer of heat through airflow rather than direct conduction, convection dryers can be more energy-efficient than conductive drying methods, leading to lower operating costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
Industrial Applications
Convection dryers find widespread use across various industries due to their efficient and uniform drying capabilities. One of the primary applications is in the food processing industry, where convection dryers are employed to remove moisture from a wide range of products, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy items. These dryers help preserve the quality and extend the shelf life of food products.
In the chemical industry, convection dryers play a crucial role in drying chemical compounds, resins, and other materials. They ensure consistent drying, which is essential for maintaining product quality and preventing degradation. The pharmaceutical industry also relies on convection dryers for drying active ingredients, excipients, and finished drug products, ensuring compliance with strict quality standards and regulations.
Minerals processing is another area where convection dryers are indispensable. They are used to dry minerals, ores, and other materials before further processing or transportation. Convection dryers help reduce moisture content to desired levels, improving efficiency and product quality. Additionally, in wastewater treatment plants, convection dryers are employed to dry sludge, reducing its volume and making it easier to handle and dispose of.
Selecting a Convection Dryer
When choosing a convection dryer for your manufacturing facility, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. One of the primary considerations is the required production rate or capacity needed to meet your throughput goals. The dryer’s capacity should align with your desired output while allowing room for future growth. Additionally, the properties of the material being dried, such as particle size, shape, and sensitivity, will influence the dryer type and configuration best suited for your application. As noted in Sinothermo’s guide, certain dryers may be more appropriate for specific materials.
Another critical factor is the energy source available at your facility. Convection dryers can be heated by various means, including gas, steam, or thermal fluid systems. Your choice of energy source will impact the dryer’s operating costs and environmental footprint. Budget constraints must also be taken into account, as convection dryers can vary significantly in price depending on their size, features, and level of automation.
The physical footprint of the dryer and its integration with existing equipment should also be evaluated. As Anatol’s guide highlights, conveyor dryers can be large pieces of equipment, and available floor space may limit your options. Additionally, consider how the dryer will interface with upstream and downstream processes for seamless material handling and production flow.
Improving Manufacturing Efficiency
Convection dryers offer several advantages that can significantly improve manufacturing efficiency and productivity. One of the primary benefits is increased throughput due to the rapid and uniform drying process. By removing moisture quickly and evenly, convection dryers can process larger batches in a shorter time frame, resulting in higher production rates compared to other drying methods [1].
Additionally, the consistent drying action leads to better product quality, as it minimizes over-drying or under-drying of materials. This consistency is crucial in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, where product quality is paramount.
Convection dryers also offer labor savings by requiring less manual intervention and handling during the drying process. Their automated operation and continuous feed systems reduce the need for frequent loading and unloading, resulting in lower labor costs.
From an energy perspective, convection dryers are generally more efficient than conductive drying methods, such as tray dryers or drum dryers. The high heat transfer rates and the ability to recirculate heated air contribute to significant energy savings [2]. This not only translates into cost savings but also reduces the environmental impact of manufacturing operations.
Furthermore, convection dryers often have a smaller footprint compared to other drying systems, allowing for more efficient use of available floor space in manufacturing facilities. This compact design can be particularly advantageous in space-constrained environments.
Top Convection Dryer Manufacturers
When it comes to leading convection dryer manufacturers, several brands stand out for their quality, innovation, and industry experience:
Andritz is a global supplier of advanced industrial drying systems, including a wide range of convection dryers for various applications. Their dryers are known for energy efficiency, precise moisture control, and robust construction.
Wenger Manufacturing is a pioneer in the design and production of conveyor dryers and other processing equipment for the food, pet food, and aquaculture industries. Their convection oven systems deliver consistent drying with minimal product degradation.
Bühler Group offers innovative convection dryers as part of their comprehensive range of processing solutions. Their DryTec line features advanced process controls and sanitary designs ideal for food, feed, and industrial materials.
FEAM maintains a reputation for building heavy-duty and customized convection dryers to meet unique drying challenges across sectors like minerals, chemicals, and environmental applications. Their fluid bed dryers provide efficient heat transfer and product movement.
Operating Costs
One of the key advantages of convection dryers is their low operating costs compared to other drying methods. According to ScienceDirect, convection dryers have low capital and running costs, making them an economical choice for many industrial applications.
Energy usage is a major factor in the operating costs of any drying system. Convection dryers are generally more energy-efficient than conductive drying methods, as they rely on hot air or steam circulation rather than direct heat transfer. Research has explored various energy sources and techniques to further improve the thermal efficiency and reduce energy consumption of convection dryers.
Maintenance requirements for convection dryers are relatively low compared to other types of dryers. The simple design with few moving parts minimizes the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Additionally, the lack of direct contact between the heating source and the material being dried reduces the risk of fouling or contamination, further reducing maintenance needs.
Labor costs associated with convection dryers are also typically lower than other drying methods. The continuous or batch processing nature of convection dryers allows for automated operation with minimal human intervention, reducing the need for extensive manual labor. This can lead to significant cost savings, especially in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Environmental Considerations
Convection dryers offer several environmental advantages over other drying methods, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and reduced emissions. According to a study by Ibrahim (2024) Applied insight: studying reducing the carbon footprint of …, using a heat-source temperature-elevating (HSTEE) convection dryer resulted in a 37-54% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to traditional drying methods.
The high energy consumption of industrial dryers can contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impacts, as noted by Kaveh et al. (2021) in their research comparing drying techniques Comparison of different drying techniques and their carbon …. Convection dryers are generally more energy-efficient than conductive or radiation drying due to their efficient heat transfer mechanisms.
Moreover, many convection dryers allow for heat recovery and energy integration, further improving their sustainability. A study by Urbano et al. (2023) Energy Performance, Environmental Impacts and Costs of … investigated the benefits of heat recovery in convective drying systems, demonstrating potential energy savings and reduced environmental impacts.
Trends and Innovations
Advancements in convection drying technologies are driven by the need for improved energy efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced product quality. One notable trend is the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar power, into drying systems. According to a review by Venkateswarlu et al. (2024), solar dryers have gained significant attention due to their potential for energy savings and sustainability.
Another area of innovation focuses on optimizing airflow patterns and heat transfer mechanisms to achieve more uniform and rapid drying. Chojnacka’s review (2021) highlights advancements in seed and grain drying systems, including the use of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations to design more efficient airflow configurations.
Emerging applications for convection dryers extend beyond traditional industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. Saini et al. (2023) discuss the potential of solar dryers in agricultural settings, particularly in developing regions, where they can provide cost-effective and sustainable drying solutions for small-scale farmers.
Ivey excels in effectively conveying company directives through impactful marketing and public relations strategies, showcasing her expertise in the field.
Email: ivey.tang@retcl.com
Phone: +86 19105155639